In recent years, carb counting has become a major point of dietary emphasis. With many low-carb diets such as keto and Atkins becoming more commonplace, it’s crucial to account for carbohydrates properly.
The problem is, there’s an ongoing debate between whether carbs or “net carbs” should be counted as part of one’s macronutrient profile. While some groups argue total carb count is a more precise measurement, others disagree with this sentiment.
Not all carbohydrates have the same effect from a dietary perspective. While some are more digestible, others tend to pass through the body without being absorbed.
It’s important to understand the differences between carbs and net carbs so that you can determine which form of measurement is most conducive to your lifestyle and goals.
Let’s take a deeper look at various types of carbs and what roles they play within your body.
Let’s Define a Carbohydrate
Before we dive into net carbs, it helps to know what a carb actually is in the first place.
Carbohydrates are an umbrella term for molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. There are two main types of carbs found in the foods we eat—simple carbs and complex carbs.
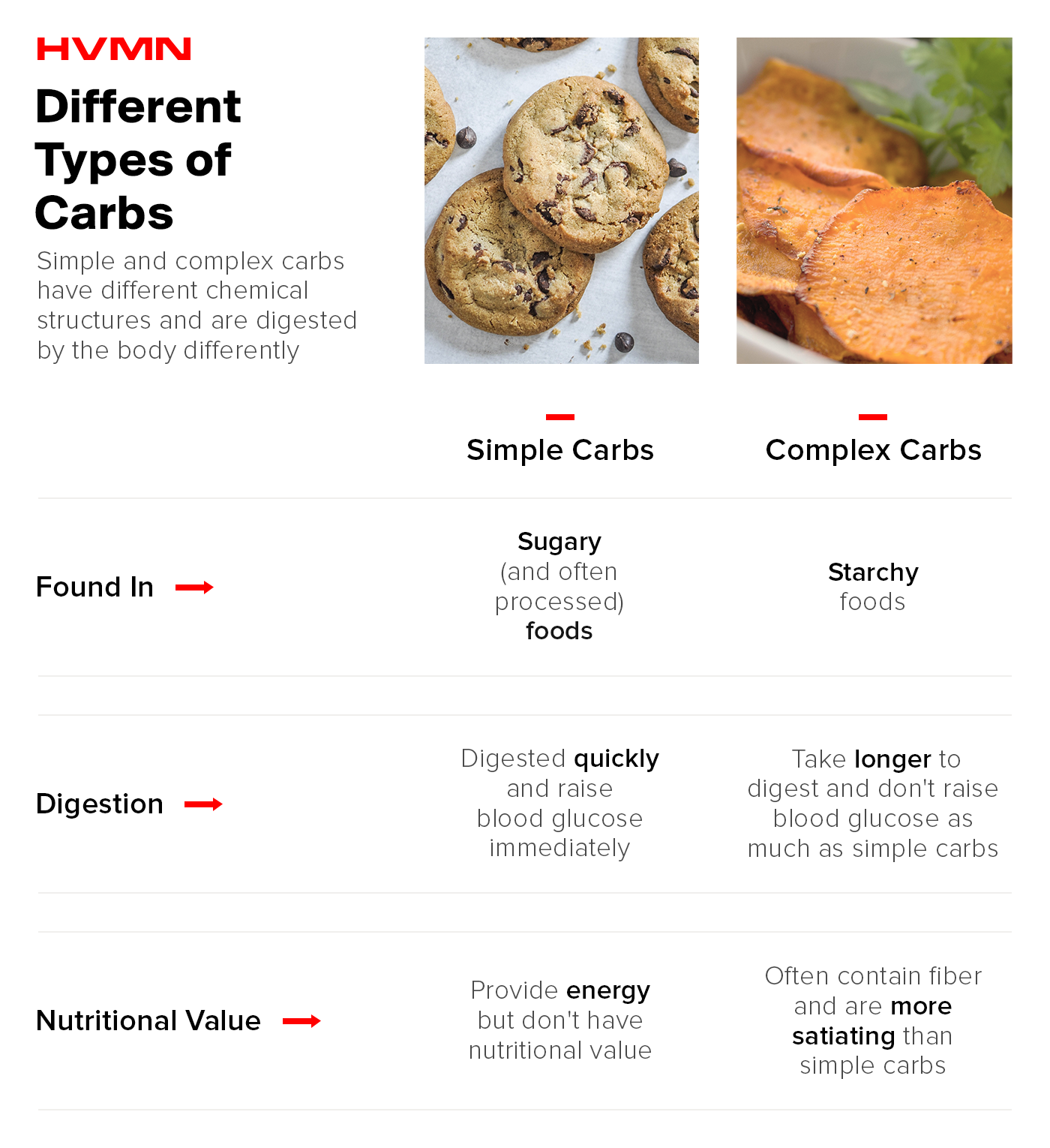
Simple carbs are found mostly in sugary foods and contain only one or two sugar unit molecules which can affect how quickly the food is digested and absorbed. Some examples are fruits and foods containing table sugar, like soda or cookies.
Complex carbs are slower-digesting in nature and contain several sugar units linked together. They are often found in whole grains, starchy vegetables, white and sweet potatoes, carrots, and oats.
While simple and complex carbs can be used as an energy source or stored as fat.
If a person consumes more carbs than needed, the body will convert excess carbs to fat.
There are other types of carbs which are not readily digestible by the body.
Fiber is different from the other two forms of carbohydrates. While it is similar in molecular profile, it does not provide a direct form of energy—it passes through the body without being digested and absorbed into the bloodstream for energy. The main role of fiber is to feed friendly bacteria in the digestive system.
Sugar alcohols also fall under the carbohydrate umbrella. They are typically used as a form of sweetener and contain only half the amount of calories as traditional carbohydrates. They are added to food as a reduced calorie sweetener and as a bulking agent.
Although each of these are considered carbs, the body handles each of them differently. It’s these differences that allow us to think that not all carbs are created equal, and we shouldn’t look at them as all playing the same role without our body.
Net Carbs Explained
Net carbs refers to carbs that are absorbed and processed by the body.
Simple and complex carbs are found in foods we eat. They are broken down in the small intestine and later become used as a source of energy in the body.
Those other types of carbs, such as fibers and sugar alcohols, can’t be broken as easily. Because our bodies don’t actually absorb these types of carbs (to use them for energy), many people subtract fibers and sugar alcohols from overall carbohydrate amount.
This is often where debate tends to arise.
While some count every single carb in their diet, others subtract fiber and sugar alcohols because the body does not retain these macronutrients in the same manner.
Why is Fiber Different?
Unlike other forms of carbohydrates, fiber is not directly used as a natural fuel source for the body. It passes directly into the colon and can’t be broken down by enzymes in the digestive tract. Because of this, less than half the total carbohydrates from dietary fiber are metabolized to glucose.
Fiber is best known for its ability to relieve constipation, especially soluble fiber (hello fruit, oatmeal, avocados and broccoli!), but can also provide several other health benefits.

Elevated fiber intake has been shown to reduce the risk of colon cancer in one study, but as mentioned earlier, this cause and effect action is now being debated among the scientific community.
Fiber consumption may be linked to lowering the risk of developing serious diseases.
The FDA Daily Value for fiber (the daily recommended amount) is 25 grams per day based on a 2000 calorie diet.
Even within fiber, there are two main types—insoluble and soluble fiber.
Insoluble Fiber
Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and can help speed the passage of bowel movements thereby preventing constipation. It contains no calories, nor does it spike blood glucose or insulin levels, and isn’t broken down by the gut.
Insoluble fiber helps keep bowel movements regular and helps maintain a healthy digestive system. It’s typically found in the stalks, skins, and seeds of foods such as whole grains, nuts, and veggies,
Common foods with insoluble fiber include:
- Beans
- Whole wheat
- Bran
- Potatoes
- Cauliflower
- Nuts
- Green beans
Insoluble fiber is an important part of a healthy diet that can help support several bodily functions.
Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber dissolves in water and is digested by bacteria in the large intestine.
One of the benefits of soluble fiber is its ability to help you feel full (and potentially, this can help you lose weight). A study performed on soluble fiber found that consuming 14g per day was associated with a 10% decrease in energy consumption (less food eaten) and weight loss of 1.9kg over a four month period.
As soluble fiber goes into your colon, it becomes short-chain fatty acids, which can help improve gut health and reduce inflammation.
If you’re on the keto diet, it can sometimes be difficult to find low-carb sources of fiber. Good thing H.V.M.N. has you covered.
Some MCT oil and collagen powders contain a base of acacia fiber, which is rich in soluble fiber. The best part? Both products contain zero net carbs, making them a no-brainer to add to your daily nutrition strategy for a great source of fiber and keto energy.
What are Sugar Alcohols?
Sugar alcohols are processed in a manner similar to fiber—they are not directly absorbed by the body. They’re found naturally in foods and can be used as low calorie sweeteners and bulking agents. Typically, they are used as sugar substitutes that contain about half the amount of calories as regular sugar.
As the name suggests, they’re a hybrid of sugar molecules and alcohol molecules.
Their chemical structure is similar to sugar, and thus have the ability to activate sweet taste receptors on your tongue. That’s part of their allure: sweet taste, far fewer calories.
You will typically find sugar alcohols in foods such as chewing gums, ice creams, frostings, cakes, cookies, candies, as well as some foods that claim to be low in carbs or sugar.
The most common sugar alcohols used today include:
- Erythritol
- Isomalt
- Maltitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
Erythritol has the least amount of net carbs. 90% of it is excreted in urine and only 10% enters the colon.
There are limited studies available on sugar alcohols, but no known studies have shown raised insulin or blood sugar levels as a result.
How to Calculate Net Carbs
If you choose to use net carbs as a basis of your dietary calculations for macronutrients, it will help to make sure you are accurately accounting for them. Net carbs are calculated differently for both fiber and sugar alcohols. Be sure to read nutrition labels closely as “net carbs” are not listed separately.

Net Carbs from Fiber
Calculating net carbs using both carbohydrate and fiber amounts is super simple.
If you are eating whole foods containing fiber, simply subtract the fiber from total carbs to calculate the net carbs.
For example, an apple contains 25g of carbohydrates and 5g of fiber. The result would be 20g of net carbs. This is a little more difficult when consuming those whole foods because they don’t have nutrition labels. But a simple online search should help you give you a pretty accurate estimation.
If you’re consuming foods with a nutrition label, both carbs and fiber should be listed and thus, net carbs easily calculated.
Net Carbs from Sugar Alcohols
In most cases, half the carbs from sugar alcohols can be subtracted from total carbs. For example, if a food contains 8g of sugar alcohols, you can subtract 4g from total carbs to determine net carbs.
One exception to the rule is Erythritol. The carbs from Erythritol can completely be subtracted from total carbs.
Most of the time, you'll be subtracting fiber from carbohydrate amount to determine net carbs. Sugar alcohols are less common, but check nutrition labels to see if what you're eating contains them, and make this part of your calculation when determining net carbs
Should You Use Net Carbs?
People debate about whether counting net carbs provides a more accurate representation compared to total carbs.
Using net carbs will allow for more dietary flexibility because you’re able to eat fiber-rich foods without consuming too many carbohydrates. There are also numerous health benefits associated with fiber consumption; a study performed on individuals who regularly consumed fiber showed improved blood sugar levels and lower cholesterol.
On the other hand, people on a keto diet may argue against net carbs because the carbohydrate amount you’re consuming may take you out of ketosis. Not all people process fiber the same way—therefore, it's important to understand what works best for your body.
People trying to avoid carbohydrate intake may tend to eat more sugar-free problems, which can lead to other health problems such as weight gain, metabolic disorders, and type-2 diabetes.
When it comes down to it, using net carbs can be an imperfect science. Using total carbs can help provide a better framework for helping you to stick to your diet. However, if you eat lots of fibrous foods such as vegetables, using net carbs may be the perfect choice for your lifestyle. Or, if you’re on keto, and you find yourself constipated, consuming more fiber might be advantageous. You may have avoided those carbs to stick to your macros, and in the process, avoided fiber as well.
No matter if you choose to use net carbs or not, always make the dietary choices that best fit your individual lifestyle and goals. The best diet will always be the one you can stick to long-term.
